Although computers need quite a few components to run properly, the processor is the most important component. This processor chip, also called the central processing unit (CPU), is the chip that handles the processing of the data the computer needs to operate. Because of its importance, some people call it the “brain” of the computer.
For consumer-level desktop and laptop computers, two processor manufacturers — Intel and AMD — lead the market by a wide margin. Intel is the better known of the two manufacturers, as it has been delivering processors since the dawn of consumer- and business-level computing. Their processors offer different numbers of cores, varying clock speeds, and other features to meet your needs.
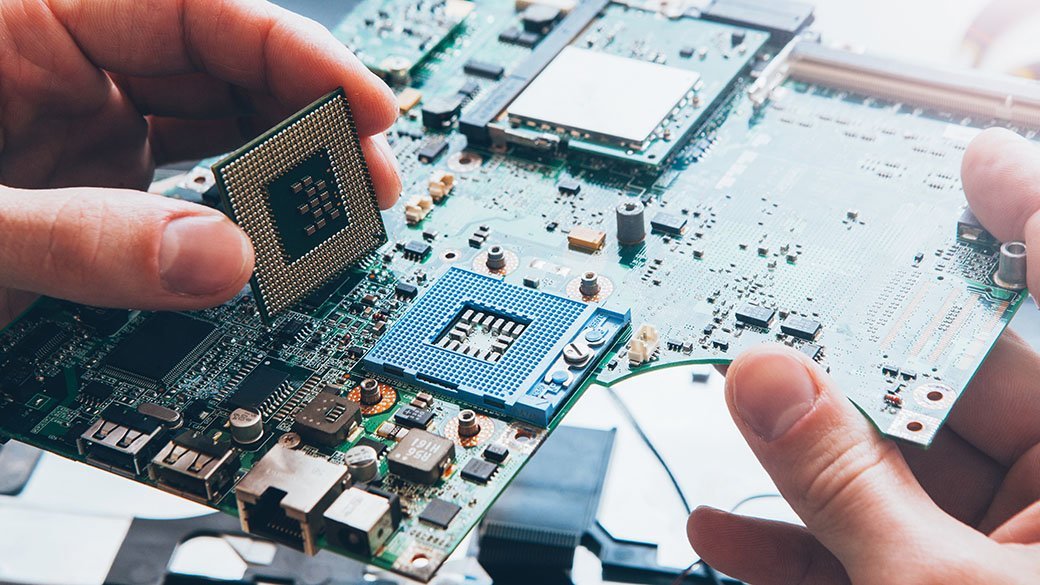
Although installing an Intel processor is not a simple process, you can affix the Intel processor to the motherboard yourself, giving your computer an instant boost in power and performance. To learn more about Intel processors and find the best option for your computing needs, continue reading our buying guide.
Key considerations
Compatibility
When you are ready to begin shopping for an Intel CPU, you need to first determine compatibility. The Intel CPU you choose must be compatible with the processor socket on the motherboard.
This is part of the reason Intel offers such a large number of CPUs. There are many different socket designs, and different Intel processors must be available to fit those sockets.
To find a compatible processor, search the internet for your motherboard and socket number. You then can figure out which Intel processors will fit in that socket.
Core processors
The primary Intel processor family for consumer-level computing is the Core family. It has a few different subfamilies.
X-series: The X-Series processor has up to 18 cores. It’s meant for extremely demanding software needs, such as high-end gaming or video editing.
i9: The i9 offers up to eight cores. It’s made for consumer-level computing needs at the upper end of the scale. This processor is useful for above-average gaming and video streaming needs.
i7: The Core i7 delivers above-average performance for general computing. It’s good for multitasking in laptops or desktops that need high clock speeds.
i5: For those with average computing needs, the i5 will serve them well. It can handle all day-to-day computing tasks efficiently. It even works nicely for average gaming needs.
i3: The Core i3 is the budget-friendly member of the Core family. It will deliver decent performance levels, but it’s not made for high-end gaming or for those who need significant multitasking capabilities.
Features
Here are some of the features you’ll want to pay attention to when comparing Intel processors.
Adaptix: With Adaptix technology, Intel processors are easier to overclock, even allowing software makers to fine-tune the performance of the CPU to the needs of the software when overclocking.
Clock speed: This measures the speed (in GHz) with which the Intel CPU processes instructions. Higher numbers signify faster performance. An Intel CPU will have a maximum clock speed listed in its specifications, but you can overclock to go beyond this number.
Cores: This is the number of individual processing sections within the overall Intel processor. Having more individual sections allows for multitasking. Don’t confuse the number of cores with Intel’s Core brand name.
DL Boost: Short for Deep Learning Boost, this technology delivers artificial intelligence features to improve the performance of Intel 10th generation processors.
Gig+: The latest generations of Intel Core processors support WiFi 6 technology, also called Gig+.
Hardware level security: In most of their processors, Intel includes a few different security features designed to protect the computing system and your data, including Software Guard Extensions (SGX), BIOS Guard, and Boot Guard.
Hyper-threading: This is Intel’s technology that allows individual cores to run two threads (or different tasks). Threading further enhances the chip’s multitasking capabilities.
Iris Plus: With Iris Plus graphics rendering technology in 10th generation Core chips, graphics rendering in 4K becomes a seamless process for a gaming setup or video streaming.
